SQL INNER JOIN
Back to home
- What is SQL INNER JOIN?
- Steps to Implement SQL INNER JOIN Query
Table of Content
 Logicmojo - Updated Aug 28, 2021
Logicmojo - Updated Aug 28, 2021
What is SQL INNER JOIN?
SQL (Structured Query Language) is a standard database language for creating, maintaining, and retrieving data from relational databases such as MySQL, Oracle, and others. A join is the result of combining a Cartesian product with a selection process. If and only if a specific join condition is met, a join operation joins two tuples from distinct relations. Only those tuples that satisfy certain constraints are included in an inner join. In this post, we'll use MySQL to demonstrate how SQL Inner Join works.
INNER JOIN
The INNER JOIN keyword selects records from both tables that have matching values.
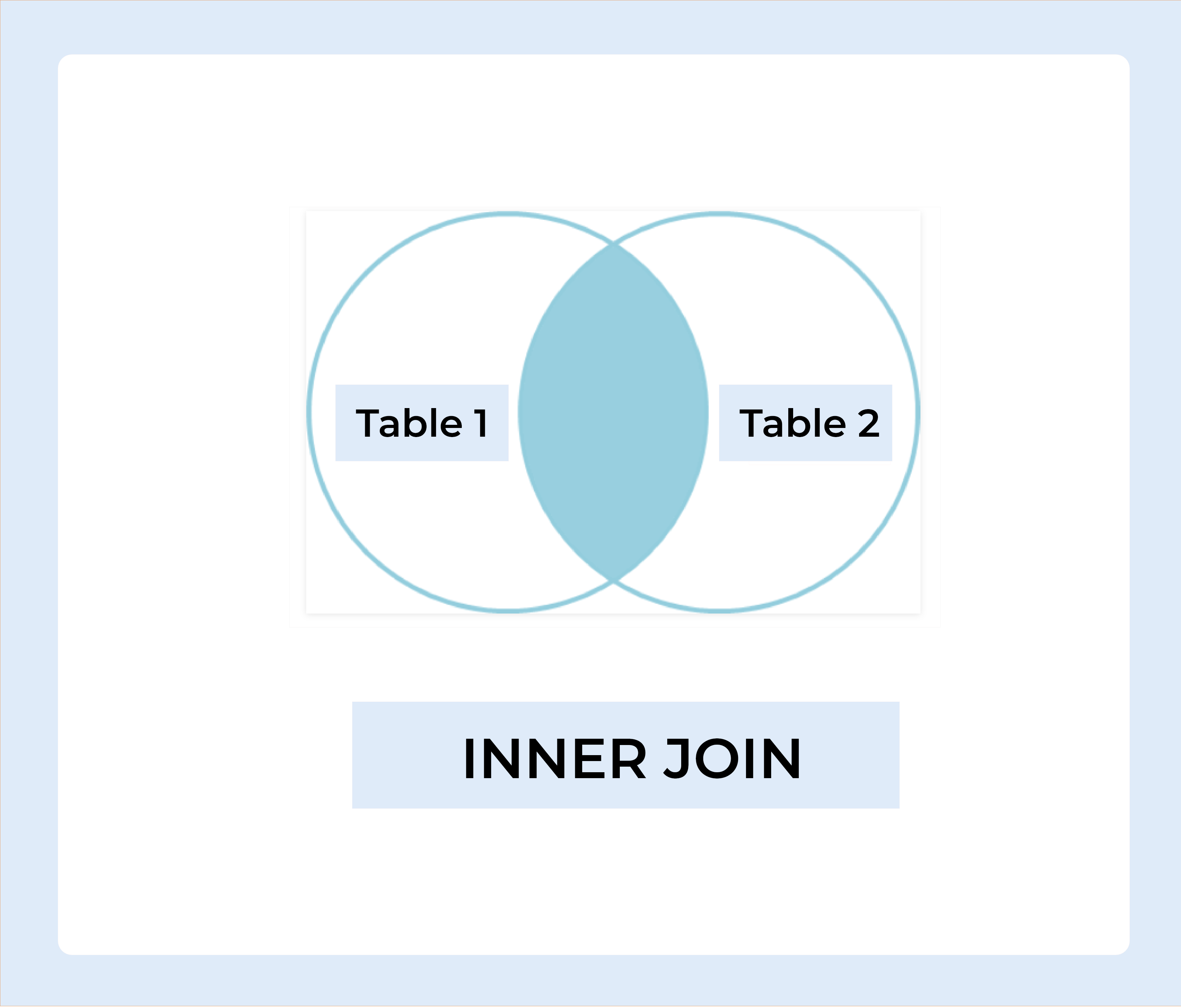
Steps to implement the SQL Inner Join
Step-1: Creating Database :Here, we'll build the database by running the following SQL query.
CREATE DATABASE logicmogo;
Step-2: Using Database :
Here, we will use the logicmojo database.
USE logicmogo;
Step-3: Adding Tables :
We will add 2 tables to the database as follows,
🚀 The first table will be the Student which will contain Roll_no, the name of the student, and their Phone no. and Age.
🚀 The second table will be Course which will contain the ID of the course,and roll number
Create Student Table :
CREATE TABLE Student(
Roll_no int,
Name varchar(20),
Phone No. int
Age int);
Create Course Table :
CREATE TABLE Course(
Course_Id int,
Roll_no int
);
Step-4: Inserting Rows :
We will insert the data in the following two tables,
Inserting rows in Student Table :
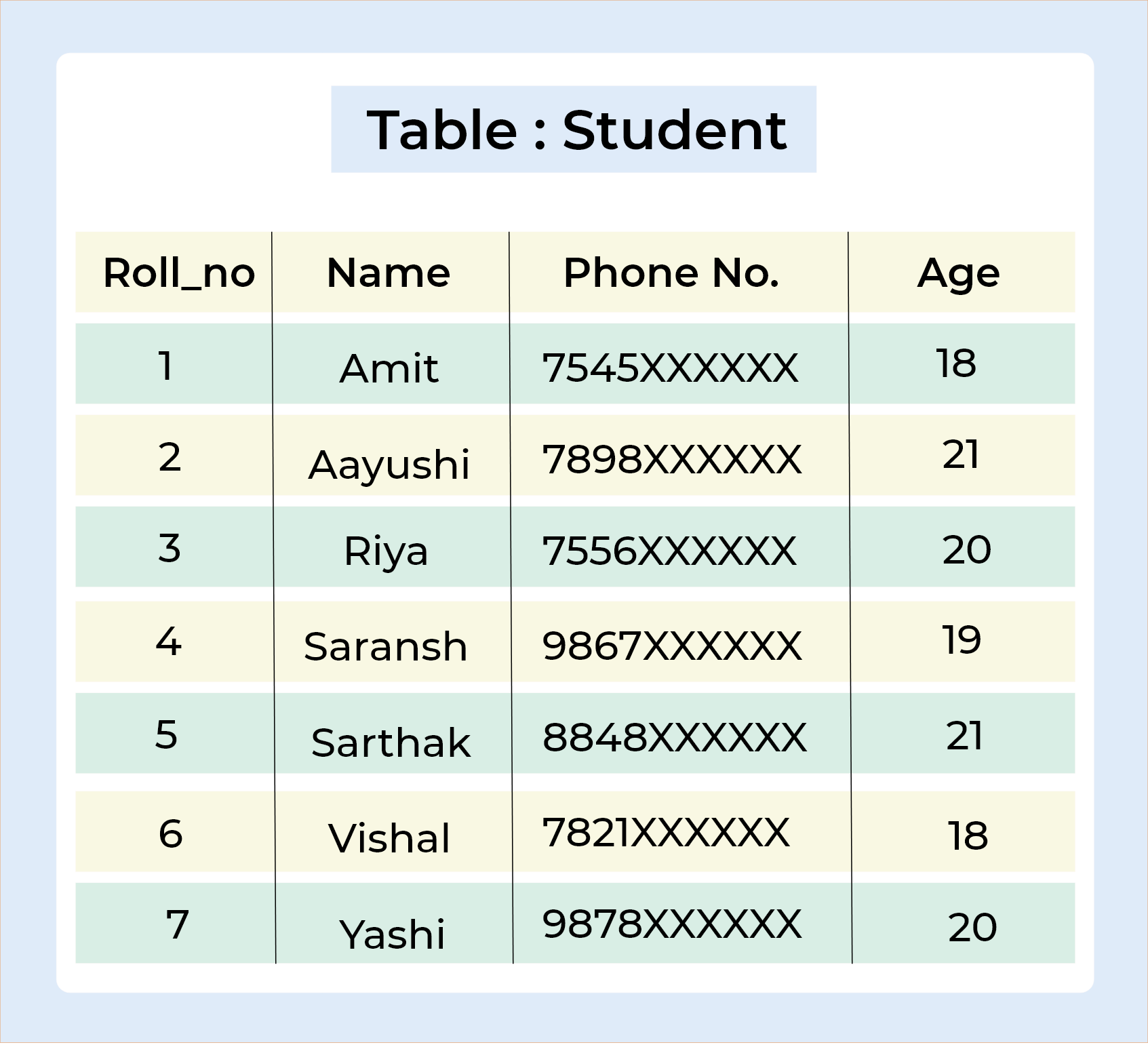
INSERT INTO Student VALUES (1, 'Amit', 7545XXXXXX, 18); INSERT INTO Student VALUES (2, 'Aayushi', 7898XXXXXX, 21); INSERT INTO Student VALUES (3, 'Riya', 7556XXXXXX, 20); INSERT INTO Student VALUES (4, 'Saransh', 9867XXXXXX, 19); INSERT INTO Student VALUES (5, 'Sarthak', 8848XXXXXX, 21); INSERT INTO Student VALUES (7, 'Vishal', 7821XXXXXX, 18); INSERT INTO Student VALUES (8, 'Yashi', 9878XXXXXX, 20);
Inserting rows in Course Table :
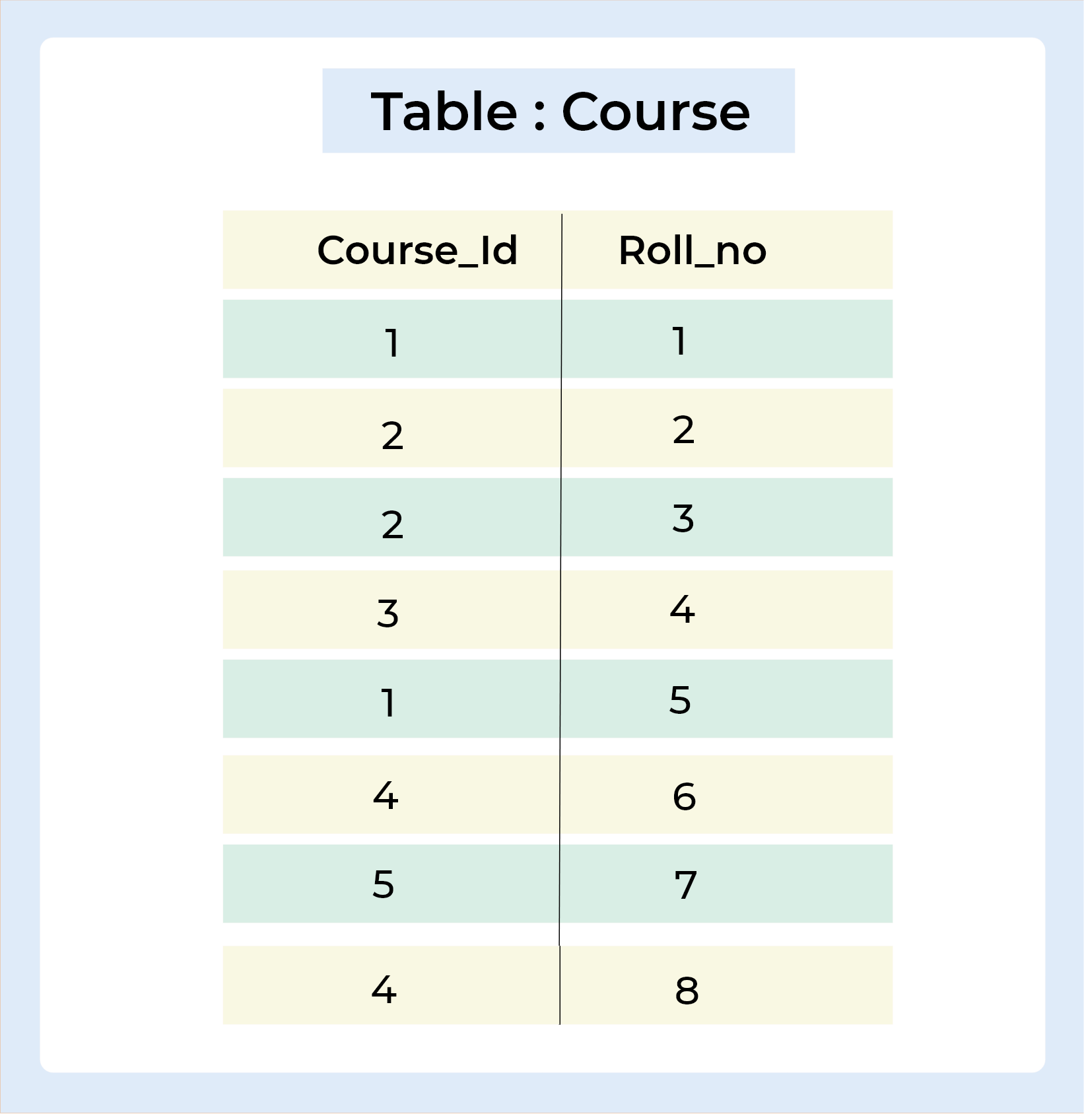
INSERT INTO Course VALUES (1, 1); INSERT INTO Course VALUES (2, 2); INSERT INTO Course VALUES (2, 3); INSERT INTO Course VALUES (3, 4); INSERT INTO Course VALUES (1, 5); INSERT INTO Course VALUES (4, 6); INSERT INTO Course VALUES (5, 7); INSERT INTO Course VALUES (4, 8);
Step-5: Status of the tables :
Verifying the data in both tables as follows.
Student Table :SELECT * FROM Student;
Output :
Course Table :
SELECT * FROM Course;
Output :
Step-6: INNER JOIN Query : INNER JOIN Syntax :
SELECT column_name(s) FROM table1 INNER JOIN table2 ON table1.column_name = table2.column_name;
Let's understand this by taking one example,
We can use the Inner Join to combine information from two tables depending on a criteria, and tuples from the Cartesian product of the two tables that do not meet the required condition are excluded from the final table.


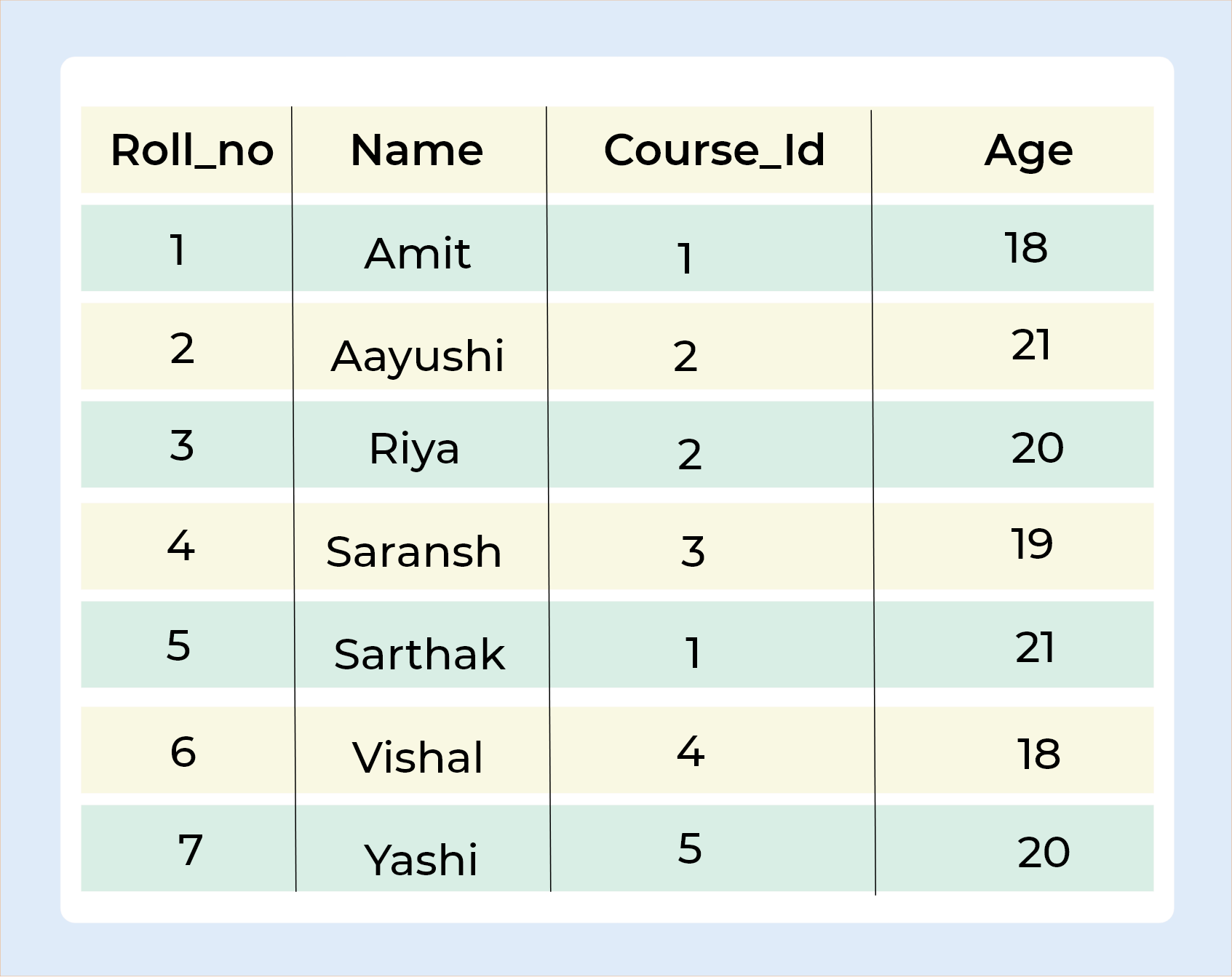
Query :
SELECT Student.Name , Student.Age, Course.Course_Id FROM Student INNER JOIN Course ON Student.Roll_no = Course.Roll_no;
Output
With this article at Logicmojo, you must have the complete idea of SQL INNER JOIN.