 Logicmojo - Updated Aug 28, 2021
Logicmojo - Updated Aug 28, 2021
What is JOIN?
A SQL Join statement joins data or rows from two or more tables together based on a common field.
The following are examples of different types of joins:
🚀 INNER JOIN
🚀 LEFT JOIN
🚀 RIGHT JOIN
🚀 FULL JOIN
INNER JOIN
The INNER JOIN keyword selects records from both tables that have matching values.
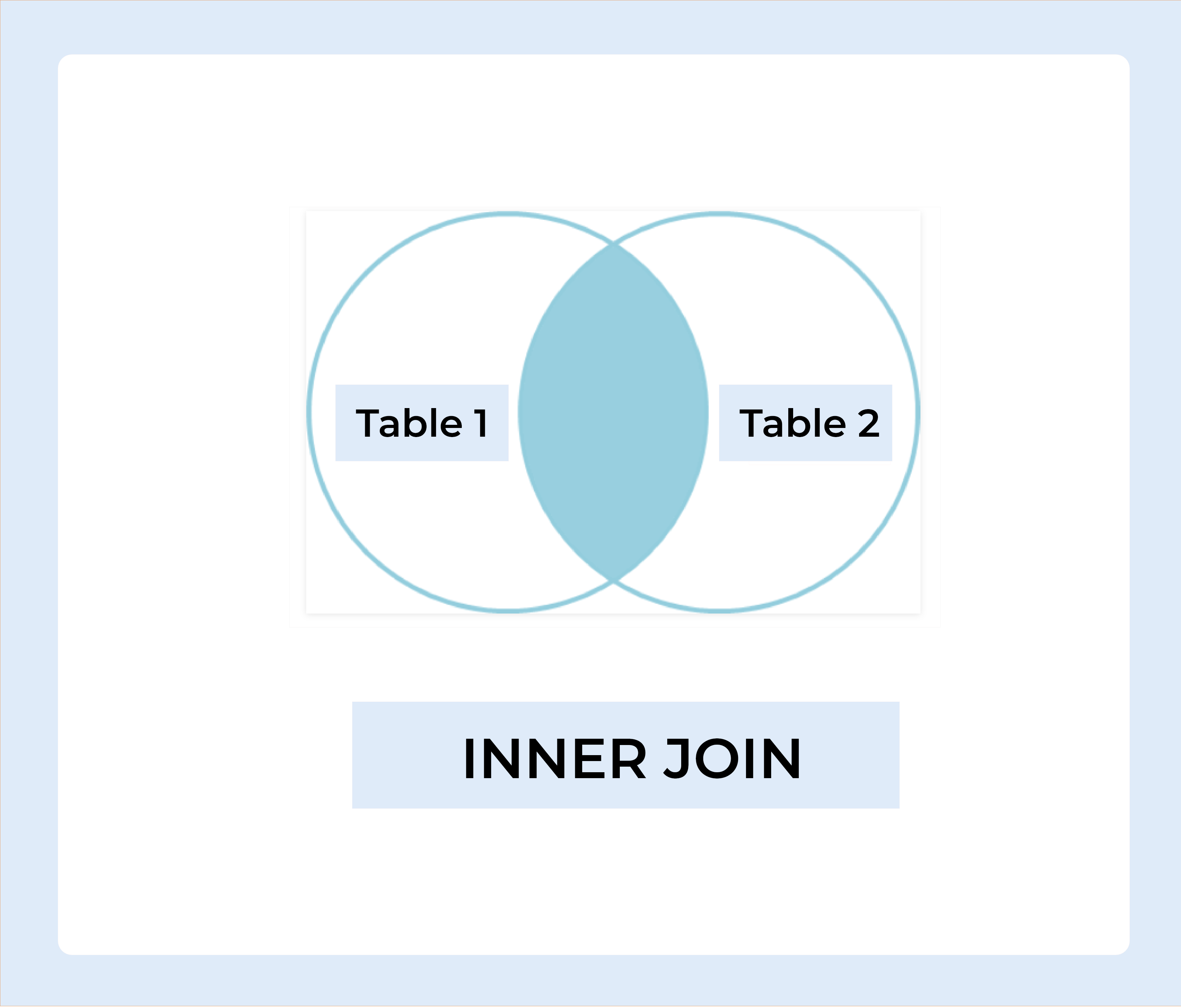
INNER JOIN Syntax :
SELECT column_name(s) FROM table1 INNER JOIN table2 ON table1.column_name = table2.column_name;
Let's understand this by taking one example,
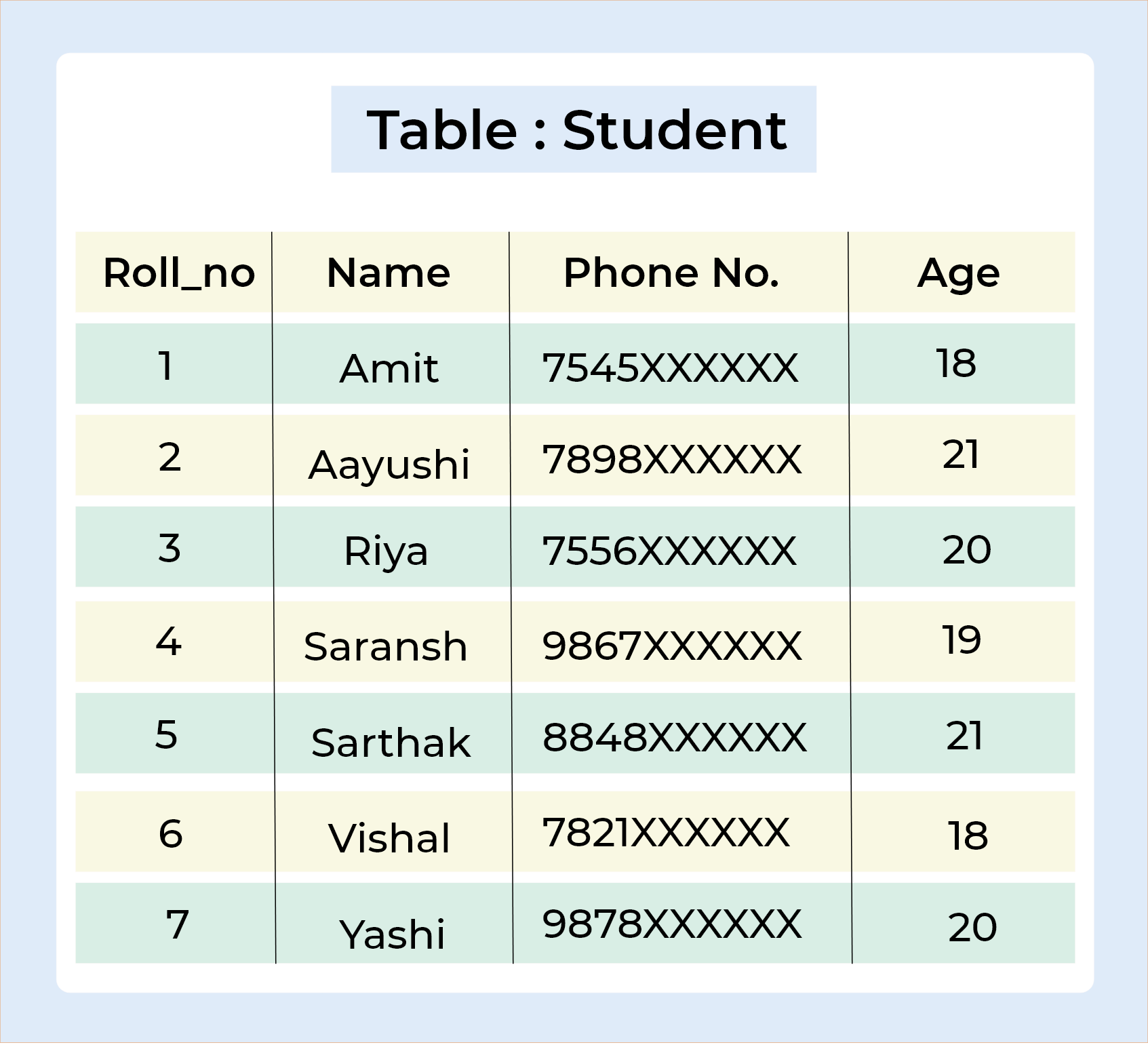
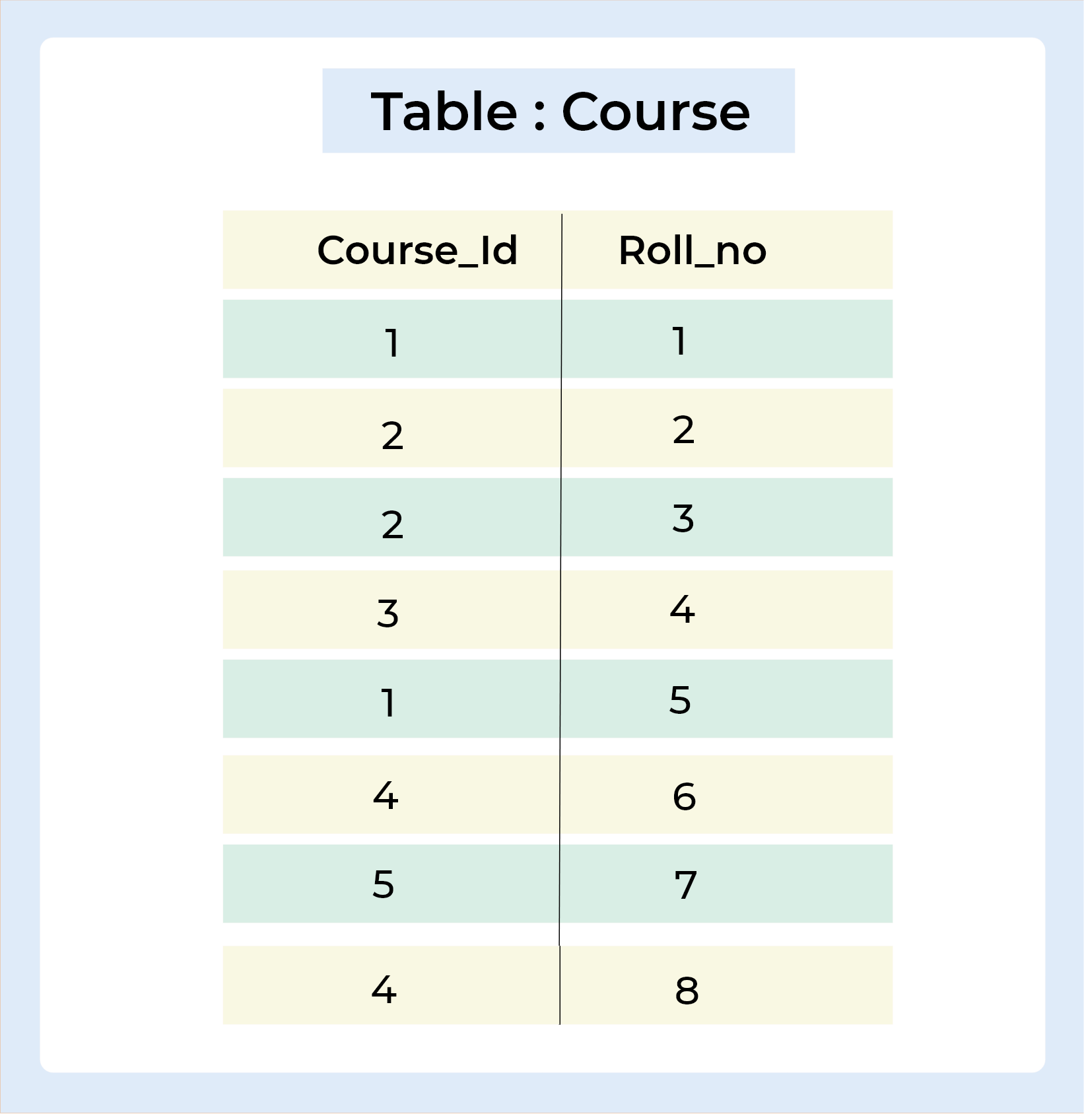
Query :
SELECT Student.Name , Student.Age, Course.Course_Id FROM Student INNER JOIN Course ON Student.Roll_no = Course.Roll_no;
Output
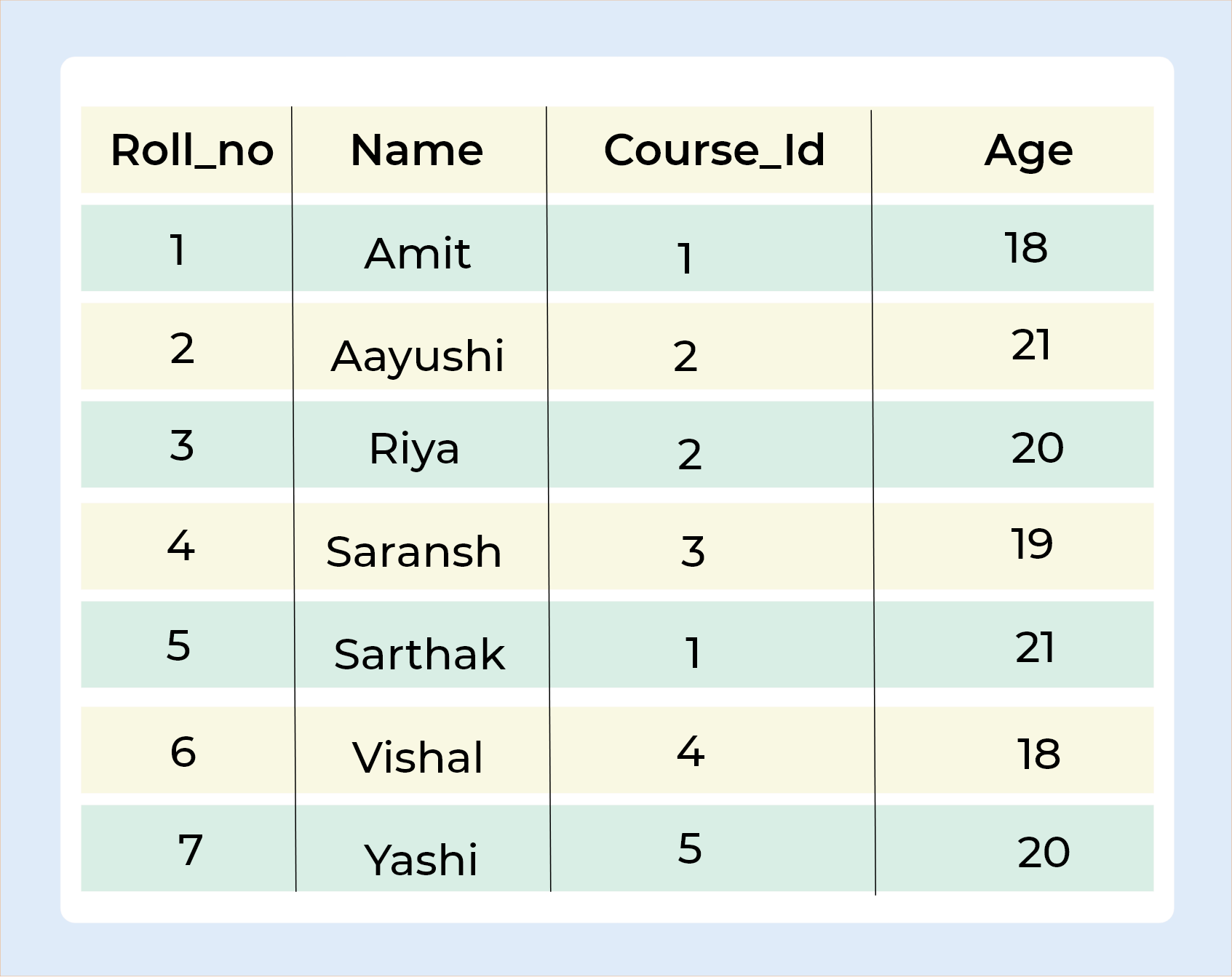
LEFT JOIN
LEFT JOIN returns all rows from the table on the left side of the join, as well as matching rows from the table on the right. The result-set will include null for the rows for which there is no matching row on the right side. LEFT OUTER JOIN is another name for LEFT JOIN.
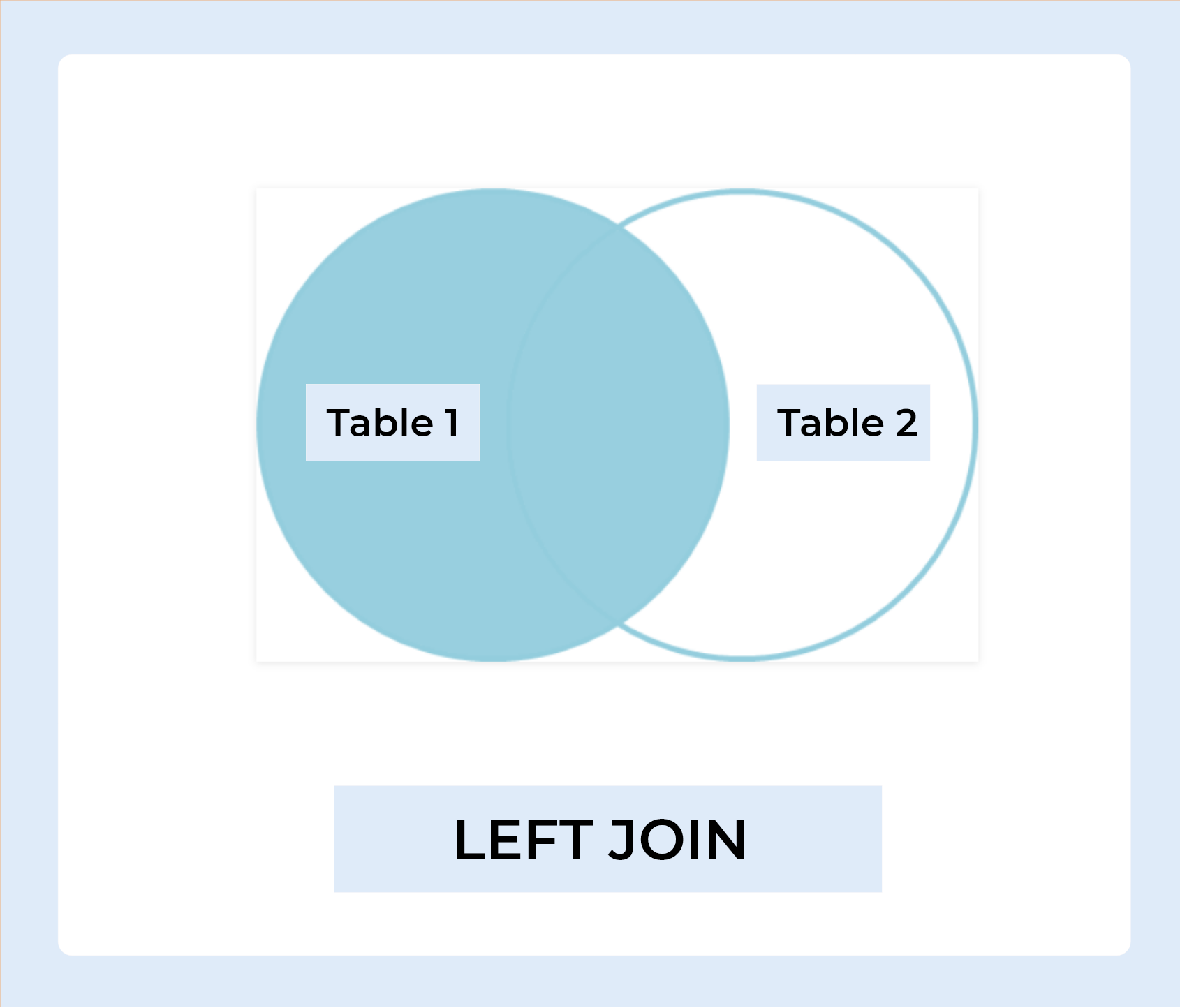
LEFT JOIN Syntax :
SELECT column_name(s) FROM table1 LEFT JOIN table2 ON table1.column_name = table2.column_name;
Let's understand this by taking one example,

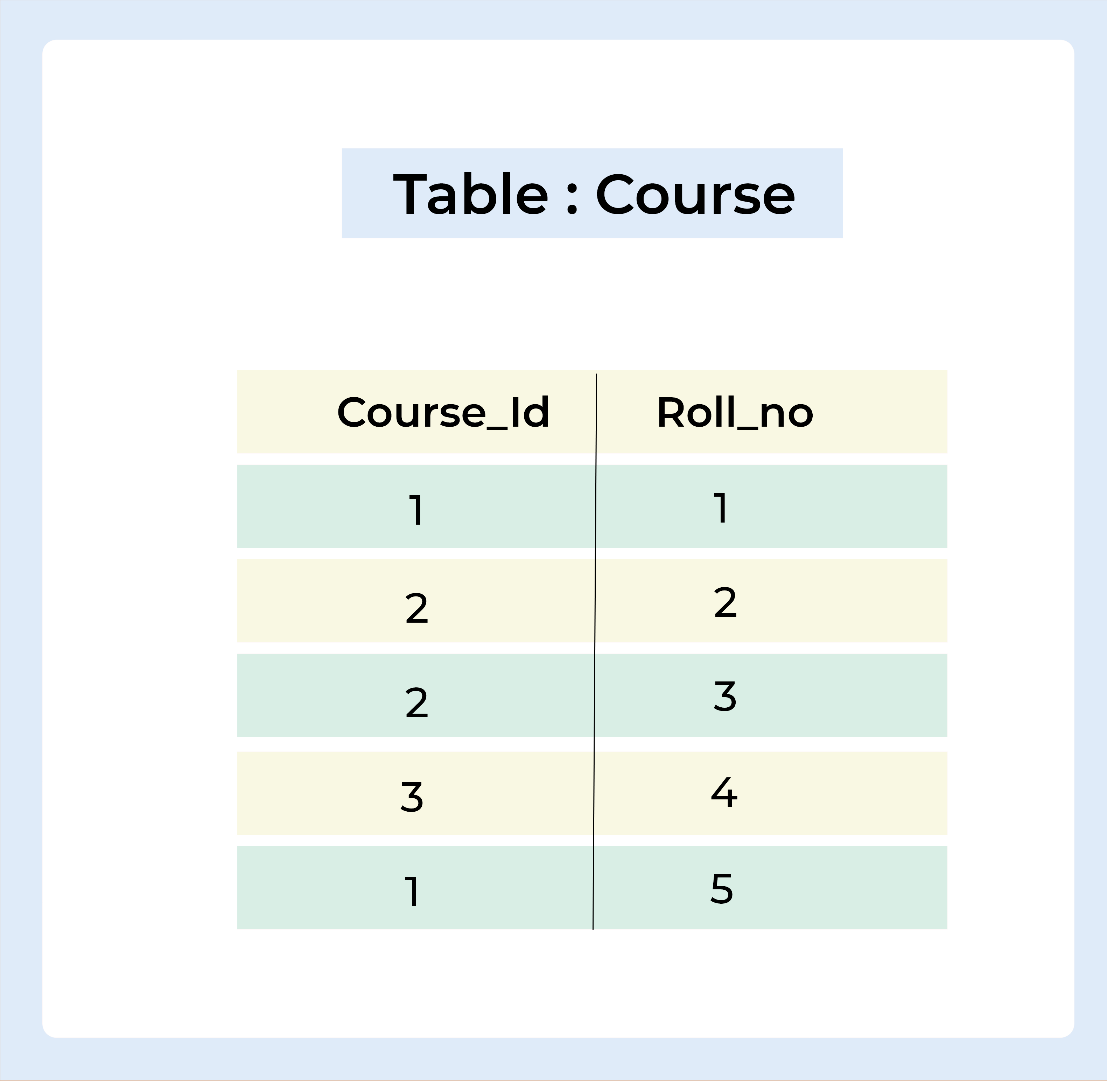
Query :
SELECT Student.Name , Student.Age, Course.Course_Id FROM Student INNER JOIN Course ON Student.Roll_no = Course.Roll_no;
Output
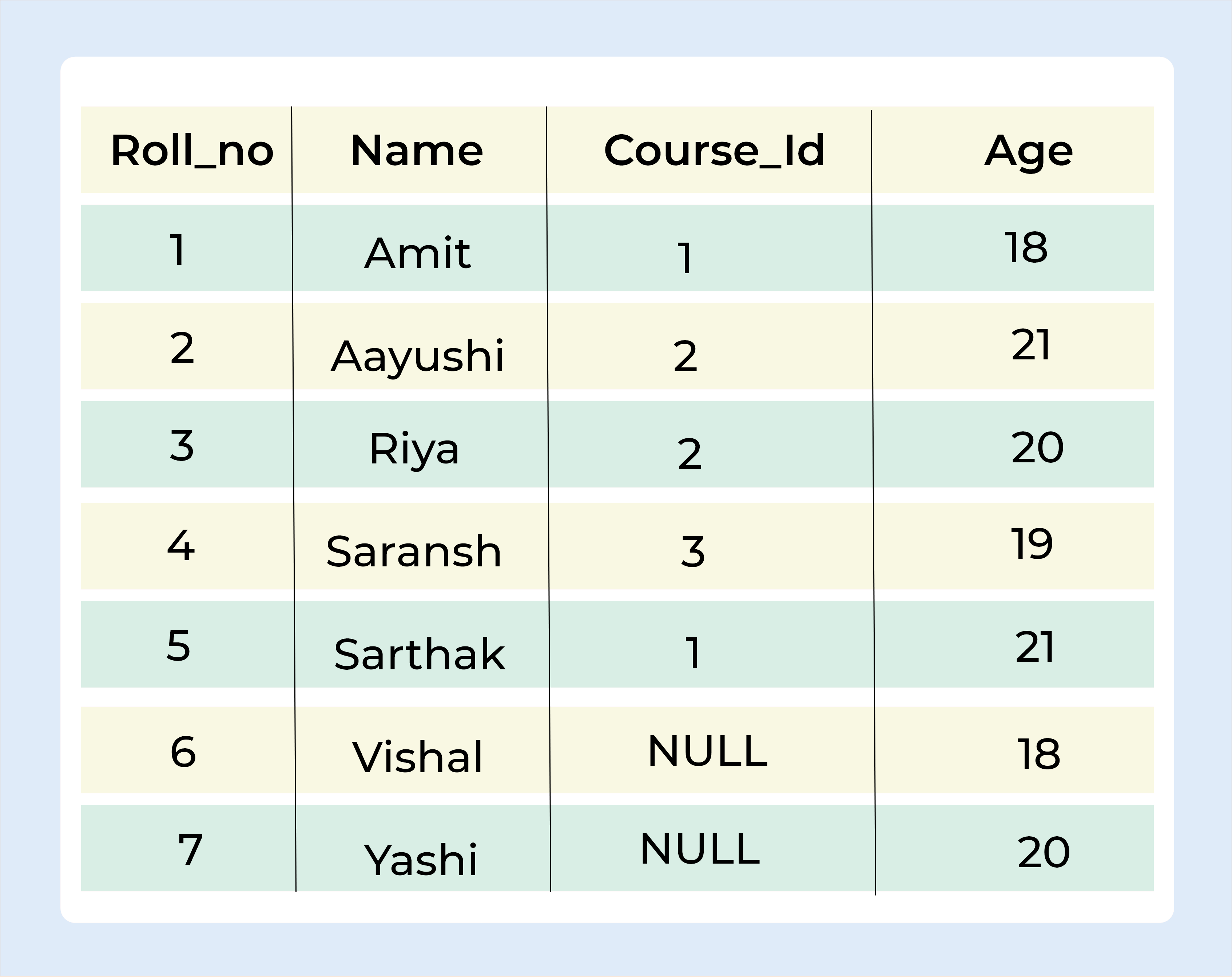
RIGHT JOIN
The RIGHT JOIN function is analogous to the LEFT JOIN function. This join retrieves all rows from the table on the right side of the join, as well as matching rows from the table on the left. The result-set will include null for the rows for which there is no matching row on the left side. RIGHT OUTER JOIN is another name for RIGHT JOIN.
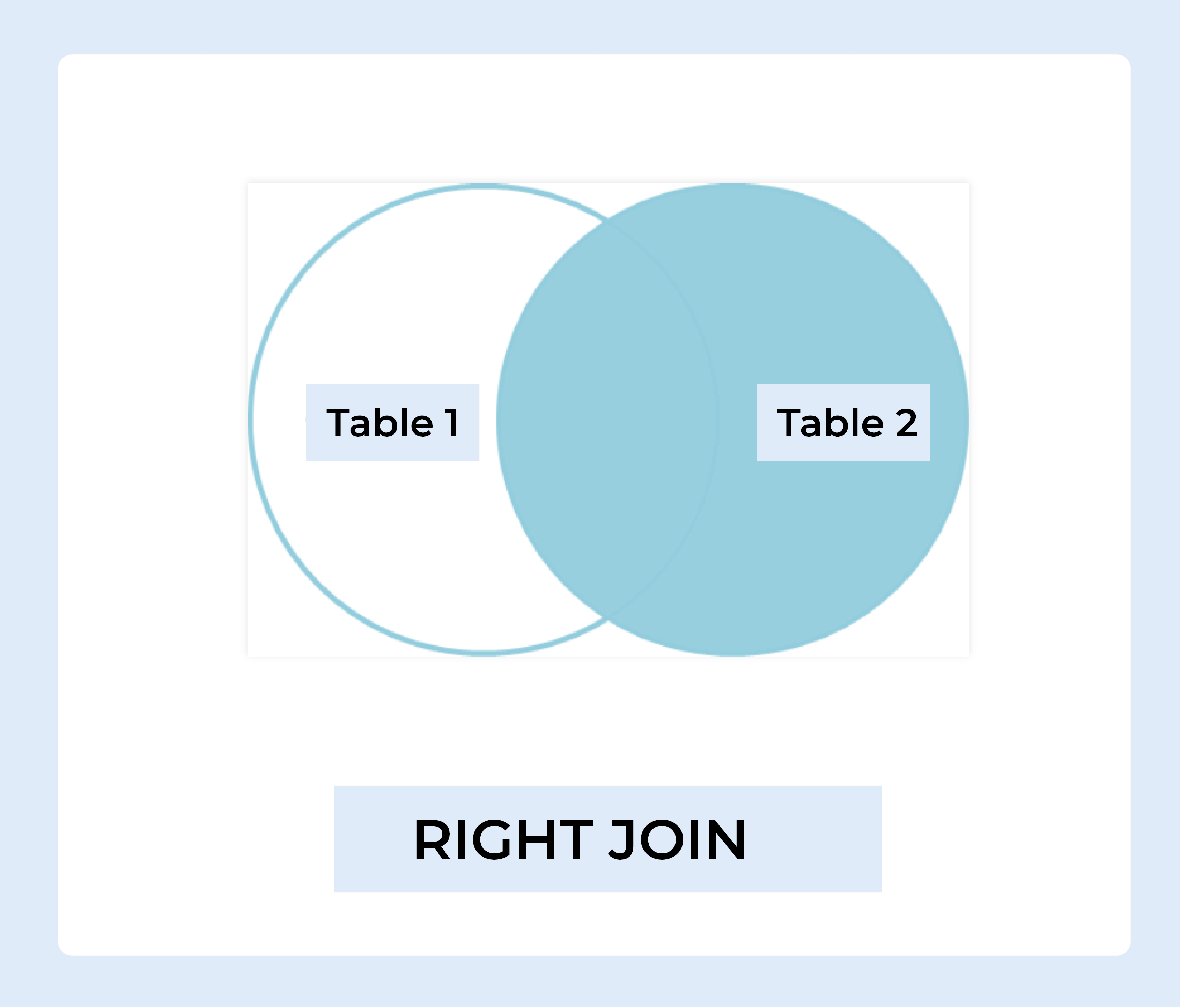
RIGHT JOIN Syntax :
SELECT column_name(s) FROM table1 RIGHT JOIN table2 ON table1.column_name = table2.column_name;
Let's understand this by taking one example,


Query :
SELECT Student.Name , Student.Age, Course.Course_Id FROM Student RIGHT JOIN Course ON Student.Roll_no = Course.Roll_no;
Output
FULL JOIN
The result-set of FULL JOIN is created by combining the results of both LEFT JOIN and RIGHT JOIN. All of the rows from both tables will be included in the result-set. The result-set will contain NULL values for the rows for which there is no match.
FULL JOIN Syntax :
SELECT column_name(s) FROM table1 FULL JOIN table2 ON table1.column_name = table2.column_name;
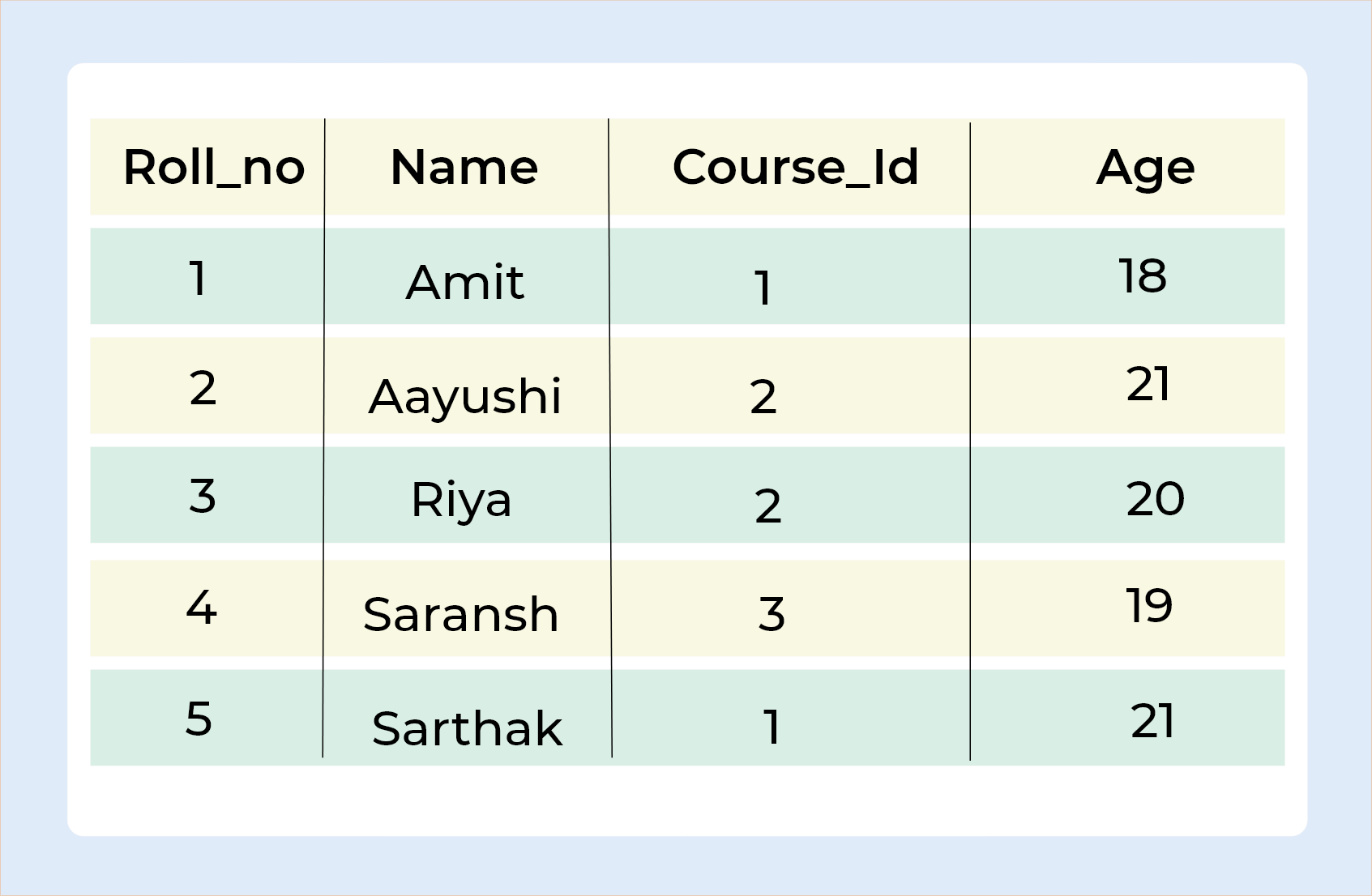
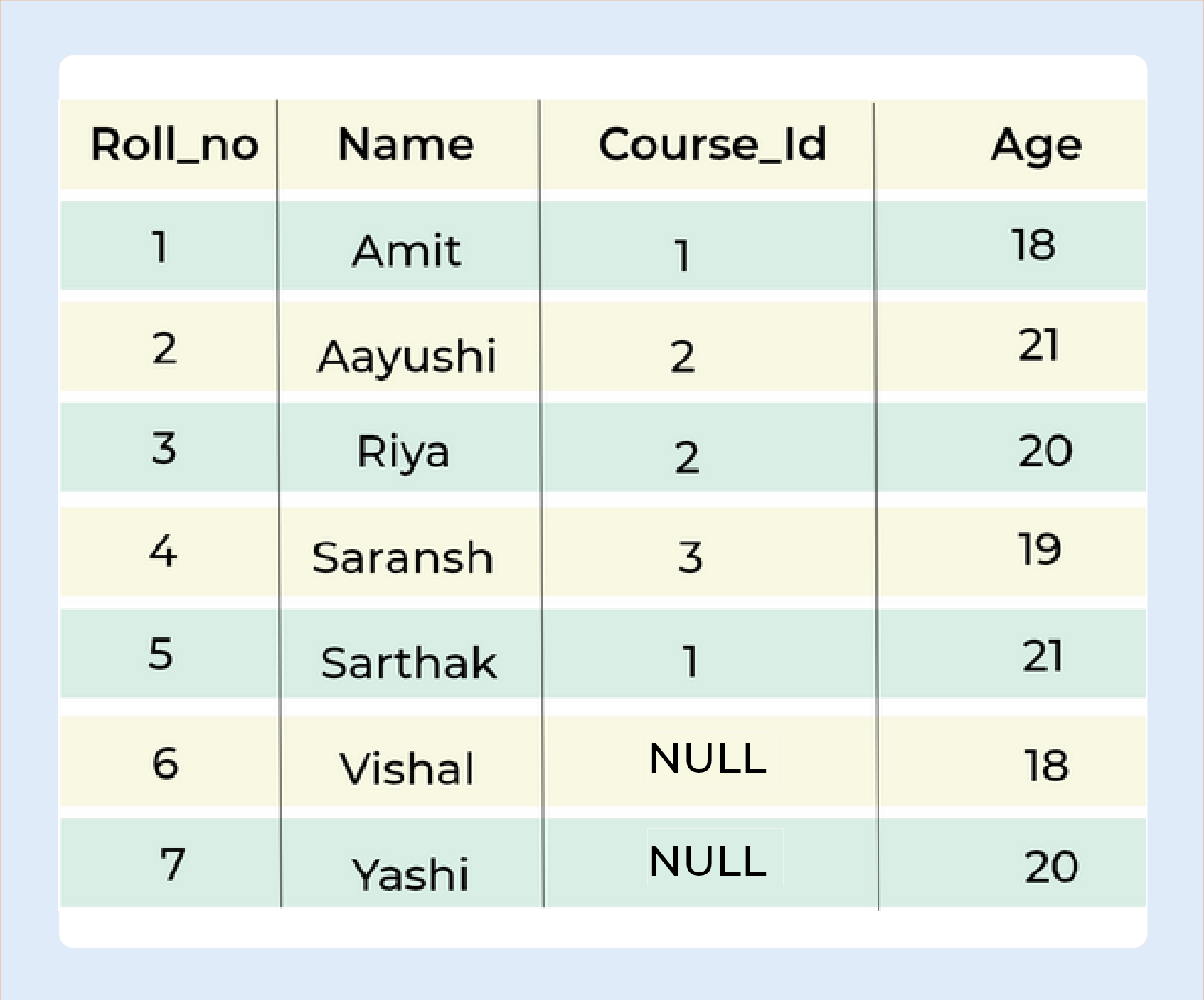
Let's understand this by taking one example,


Query :
SELECT Student.Name , Student.Age, Course.Course_Id FROM Student FULL JOIN Course ON Student.Roll_no = Course.Roll_no;
Output
With this article at Logicmojo, you must have the complete idea of SQL JOIN.
