Examples Of AI (Artificial Intelligence)
Discover how AI is transforming our daily lives through real-world applications and innovative solutions
Start Exploring
Discover how AI is transforming our daily lives through real-world applications and innovative solutions
Start Exploring
AI, short for artificial intelligence, is a fascinating concept that refers to machines endowed with the ability to think and learn much like us humans do. It involves the development of computer programs that simulate human thinking processes and problem-solving techniques. These programs are meticulously crafted to analyze vast amounts of information, identify recurring patterns, and autonomously make decisions or predictions without significant human intervention.
The primary objective behind AI technology is to empower machines with heightened intelligence, enabling them to process and comprehend data in a manner similar to our own cognitive abilities.
This endeavor entails teaching computers to discern patterns, absorb knowledge from their experiences, and base their decisions on the insights they have acquired. To achieve this, extensive data is fed into these systems, training them to identify correlations and make accurate predictions.
The ultimate aim of AI is to create machines capable of performing tasks that typically require human intelligence. These tasks encompass a wide range of abilities, including understanding natural language, recognizing and interpreting images, and making informed judgments.
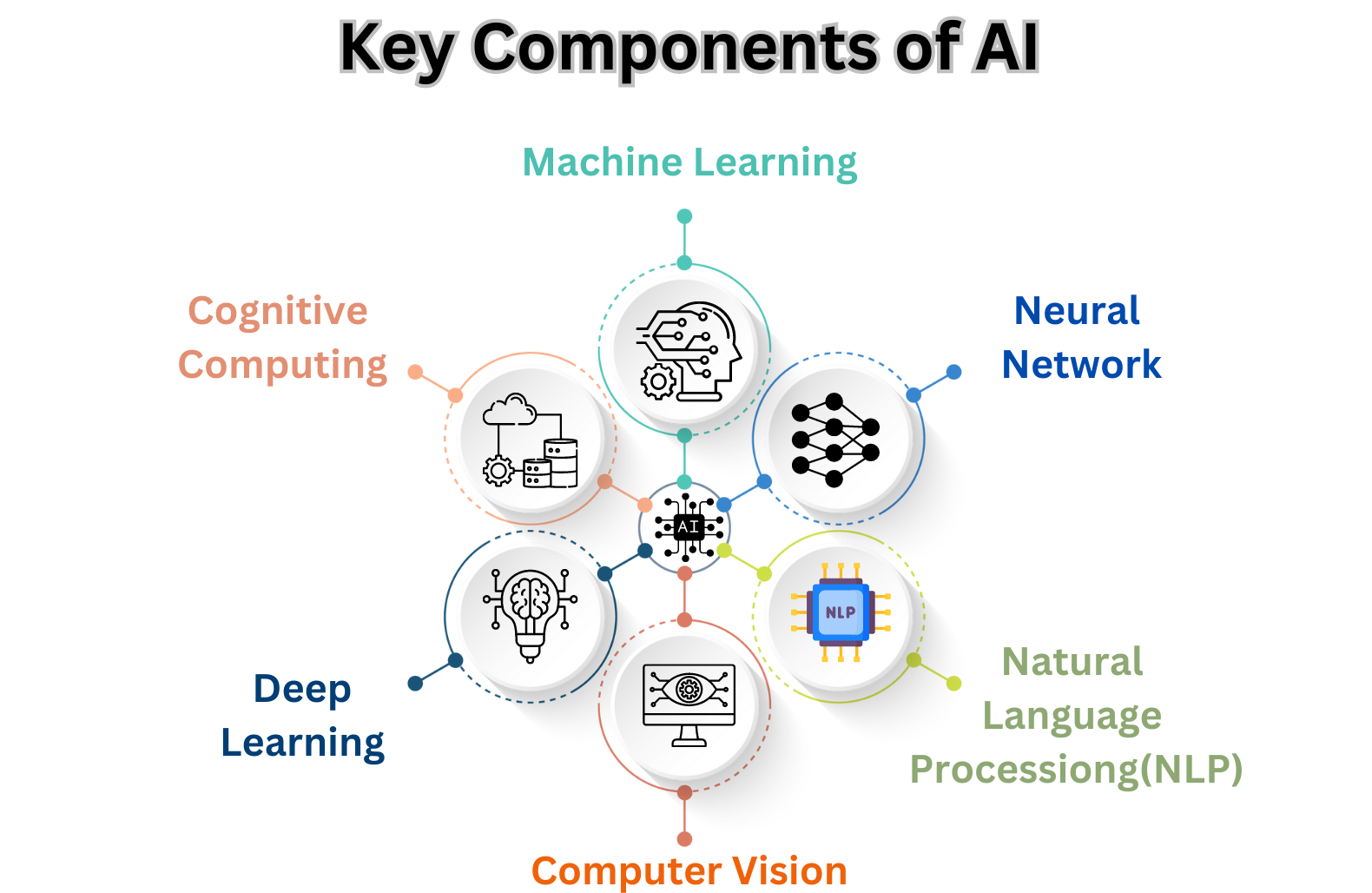
The term "artificial intelligence" (AI) refers to a broad variety of technologies that enable machines to perform jobs that previously required human intelligence. It includes a wide range of skills like:
AI systems are intended to gain knowledge through experience, adjust to new inputs, and improve their performance over time. Some key aspects include:
AI makes it possible to automate boring and repetitive operations, freeing up human resources to work on more challenging and innovative projects.
AI is excellent at quickly and accurately evaluating enormous amounts of data, finding patterns and trends that humans might not see.
AI makes it possible to have tailored experiences by comprehending and adjusting to each user's preferences.
AI systems are excellent at making decisions and solving problems by processing information and producing optimal solutions.
Chatbots and virtual assistants powered by AI offer immediate and individualized customer help.
AI technology is used in security applications including fraud detection, biometric identification, and facial recognition.
Also referred to as weak AI, Narrow AI is designed to excel at specific tasks or domains. It focuses on solving well-defined problems and performs them with a high level of proficiency. Examples include voice assistants like Siri and Google Assistant, image recognition systems, and recommendation algorithms.
General AI aims to replicate human-level intelligence and possess the ability to perform any intellectual task that a human being can. While researchers strive to achieve it, we have not yet realized fully functioning General AI systems. The goal is to develop AI that can reason, learn, and adapt across a wide range of tasks and contexts.
Superintelligent AI represents a level of AI that surpasses human intelligence. This concept raises intriguing possibilities and concerns. Superintelligent AI would not only match human cognitive abilities but potentially outperform humans in almost every intellectual task.
AI has significantly advanced the healthcare sector in a number of areas, including patient care, medication development, personalized treatment, and diagnostics.

AI has had a significant impact on the transportation industry, especially with self-driving automobiles and navigation systems.
Modern chatbots powered by AI are transforming how we interact online.

AI automates monotonous processes, optimizes operations, and boosts overall efficiency. This reduces the need for manual involvement, speeds up procedures, and reduces human error.
Large-scale data analysis, pattern recognition, and insight generation enable decision-makers to make more precise and informed choices.
Businesses can automate repetitive tasks, freeing up human resources for more challenging and innovative projects that require critical thinking.
AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants provide instant, personalized customer service that immediately responds to concerns and increases satisfaction.
Automation may replace human workers in certain roles
AI can perpetuate existing societal biases
Extensive data collection raises privacy issues
Difficulty in assigning responsibility for AI decisions
Join our comprehensive courses and crack your next tech interview with confidence!
Explore Our CoursesOne real-life example of AI is virtual voice assistants like Amazon's Alexa, Apple's Siri, or Google Assistant. These AI-powered assistants use natural language processing and machine learning algorithms to understand user commands and provide appropriate responses.
They can perform tasks such as setting reminders, playing music, answering questions, and controlling smart home devices, showcasing AI's capabilities in understanding human language and providing intelligent interactions.
Autonomous vehicles (self-driving cars) are one of the best examples of AI. They use various AI technologies including computer vision, machine learning, deep learning, and reinforcement learning.
These vehicles have advanced sensors like cameras, lidar, radar, and GPS to collect real-time data. AI algorithms process this data to detect objects, understand traffic signals, and make instantaneous decisions for safe navigation.
1. Reactive Machines: The most basic type that operates purely in the present moment with no memory or learning capability. Example: IBM's Deep Blue chess computer.
2. Limited Memory: Can retain and recall specific past experiences. Example: Self-driving cars that use sensors and past data for navigation.
3. Theory of Mind: Systems that can understand mental states of others (still in research phase).
4. Self-Awareness: The highest level with consciousness and self-awareness (purely theoretical at present).
John McCarthy is widely regarded as the "Father of Artificial Intelligence." He coined the term "Artificial Intelligence" in 1956 when he organized the Dartmouth Conference, marking the birth of AI as a field of study.
McCarthy developed the programming language LISP, worked on AI planning systems, and formalized the concept of "circumscription" for reasoning about non-monotonic logic. His pioneering work and visionary insights have left an indelible mark on the field of AI.