 Logicmojo - Updated Jan 2, 2025
Logicmojo - Updated Jan 2, 2025
Introduction
In Java, a string is a sequence of characters that behaves like an entity. After arrays, the string is one of the most prevalent and widely used data structures. It is a character array object that holds data. Consider a string to be a character array in which you can solve many string-based issues.
The String class from the Java programming language is required to make a string object. A string in Java code is represented by UTF -16. Strings are immutable, which means that their internal state stays constant even after the object has been completely created. The string object can perform a variety of operations, but the most commonly used utility in Java is reverse strings.
What is String in Java?
Strings are commonly used data structures by Java developers and thus play an important role in programming. The string is an object that depicts a character sequence. A string's fundamental feature is to store a text (set of characters) inside a quote. Strings are immutable because once a value is given to them, it cannot be changed. The String class is used to execute string creation and manipulation functions. Strings have the following essential properties:
Strings are immutable
Strings are kept in a specific memory location called the String Pool within the Java memory.
Strings are combined with the "+" operator, allowing for operator overloading.
The "==" expression cannot be used to compare strings. The equals() function is used to compare strings.
Java provides two classes for working with modified strings: StringBuffer and StringBuilder.
Reverse a string in Java
Lets understand what really reverse in string is with an example: -
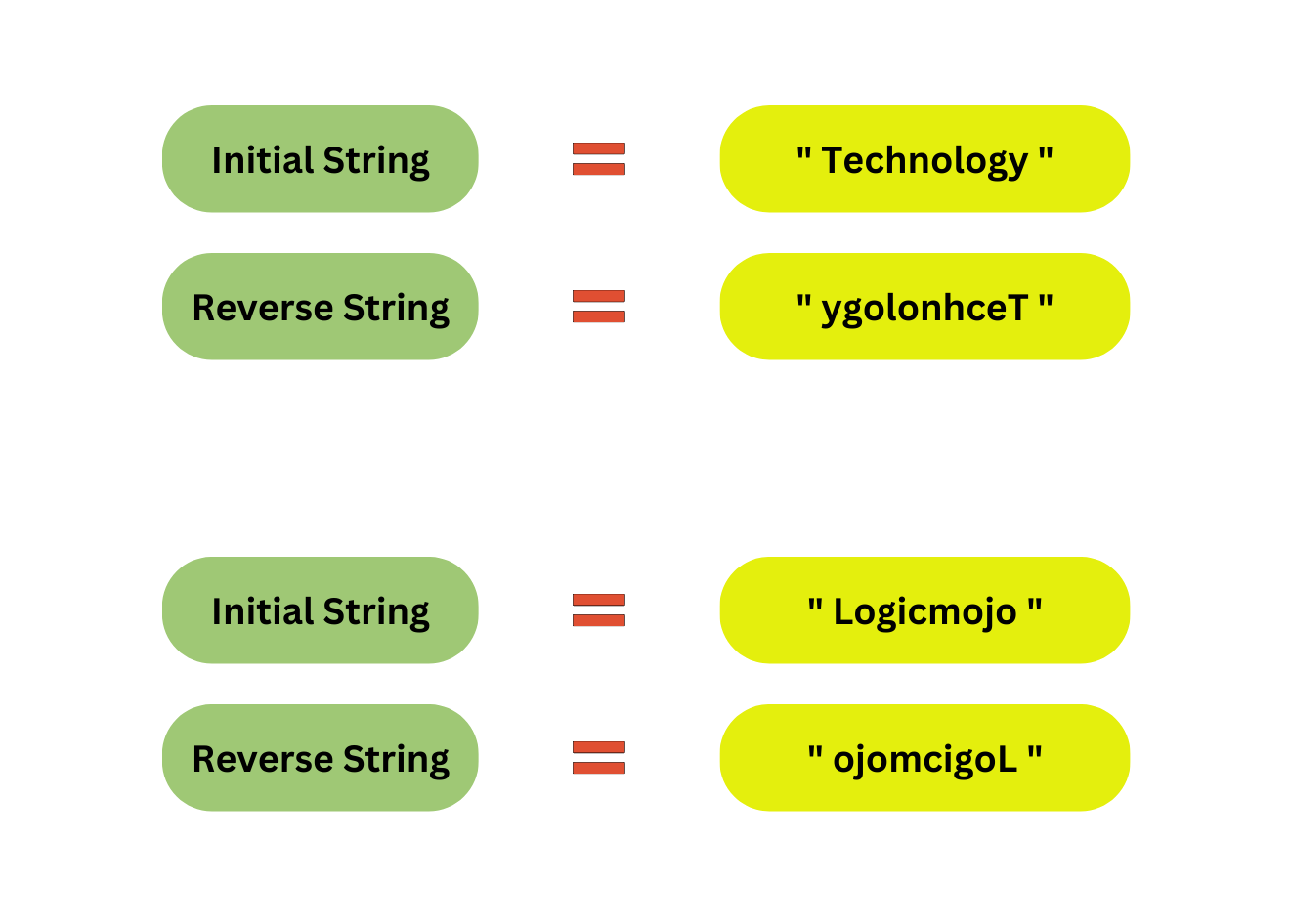
How to Reverse String in Java?
The following are the most popular methods for reversing a string in Java :
1. By Using StringBuilder
Let's look at how to use the StringBuilder class to reverse a text. The StringBuilder or StringBuffer class includes a reverse() function for reversing the characters in the string. This technique replaces the character sequence in reverse order. In Java, the reverse method is a static function that has the logic to reverse a string.
The StringBuilder class entity is used in the following code.
StringBuilder objects are mutable, memory economical, and execute quickly. However, it deems these objects to be thread-insecure.
To obtain the intended result, the object invokes the built-in reverse() method. This is the preferred technique for reversing a string in Java.
Code Implementation
import java.lang.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class reversestring
{
public static void main(String[] arg) {
// declaring variable
String input = "Logicmojo";
System.out.println("Initial string: "+input);
// creating StringBuilder object
StringBuilder value = new StringBuilder();
// append a string into StringBuilder value
value.append(input);
// reverse is inbuilt method in StringBuilder to use reverse the string
value.reverse();
// print reversed String
System.out.println( "Reverse String is : " +value);
}
}
Output
Initial string: Logicmojo Reverse String is : ojomcigoL
Alternatively, comparable to the StringBuilder, you can use the StringBuffer class reverse() method. To reverse a string in Java, both the StringBuilder and StringBuffer classes work in the same manner. In terms of reverse, both have the same strategy. However, the StringBuilder class is far more appreciated and favoured than the StringBuffer class. The StringBuilder class is quicker and does not require synchronisation. These StringBuilder and StringBuffer classes construct a mutable character series. The reverse() method will assist you in achieving the intended result.
Because the String class is immutable, string manipulation in Java will result in the creation of new string instances. StringBuilder and StringBuffer are two utility classes in Java that manage string manipulation resource sharing.
2. By Using StringBuffer
Because the String class needs a reverse() function, the input string must first be converted to a StringBuffer using the StringBuffer method. The string is then reversed using the reverse() technique.
Code Implementation
import java.lang.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class reversestring {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String string = "Logicmojo";
System.out.println("Initial string: "+string);
// conversion from String object to StringBuffer
StringBuffer sbuffer = new StringBuffer(string);
// To reverse the string
sbuffer.reverse();
System.out.println("Reverse String is : "+sbuffer);
}
}
Output
Initial string: Logicmojo Reverse String is : ojomcigoL
3. By Using CharArray()
The code below will show you how to reverse a text. One way for reversing a string in Java is to use the toCharArray() method. The code also makes use of the length variable, which returns the entire length of the string variable.
The for loop iterates until the string number zero is reached.
Code Implementation
import java.lang.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class reversestring
{
public static void main(String[] arg) {
// declaring variable
String stringinput = "Logicmojo";
// convert String to character array
// by using toCharArray
char[] array = stringinput.toCharArray();
//iteration
for (int x = array.length - 1; x >= 0; x--)
// print reversed String
System.out.print(array[x]);
}
}
Output
Initial string: Logicmojo Reverse String is : ojomcigoL
4. By Using ArrayList Object
Using the built-in function toCharArray(), convert the input string into a character array. Then, in the ArrayList object, append the characters from the array. The Collections class in Java also has a built-in reverse() method. Because the Collections class's reverse() function requires a list object, use the ArrayList object, which is a list of characters, to reverse the list.
In the code below, copy the String values to an ArrayList object. Then, on the ArrayList object, use the listIterator() function to create a ListIterator object. Use the ListIterator object to iterate over the collection. It also aids in iterating through the reversed list and displaying each object one by one to the output screen.
Code Implementation
import java.lang.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
// Class of ReverseString
class reversestring {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String value = "Logicmojo";
char[] str = value.toCharArray();
List<Character> revString = new ArrayList<>();
for (char c : str)
revString.add(c);
Collections.reverse(revString);
ListIterator li = revString.listIterator();
while (li.hasNext())
System.out.print(li.next());
}
}
Output
Initial string: Logicmojo Reverse String is : ojomcigoL
5. By Converting a String to Bytes
The getBytes() function splits or converts a string into bytes. The length of the temporary byte array will be identical to the length of the given string. Reverse the bytes and put them in another byte array.
In the code below, a byte array is formed temporarily to handle the string. getBytes() is another built-in function for converting strings to bytes. Two byte arrays are formed, one to hold the converted bytes and the other to hold the result in reverse order.
Code Implementation
import java.lang.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class reversestring {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String input = "Logicmojo";
System.out.println("Initial string: "+ input);
// getBytes() method to convert string into bytes[].
byte[] strAsByteArray = input.getBytes();
byte[] result = new byte[strAsByteArray.length];
// Store result in reverse order into the
// result byte[]
for (int i = 0; i < strAsByteArray.length; i++)
result[i] = strAsByteArray[strAsByteArray.length - i - 1];
System.out.println("Reverse String is : " +new String(result));
}
}
Output
Initial string: Logicmojo Reverse String is : ojomcigoL
6. By Using While Loop or For Loop
Simply manage the string within the while loop or the for loop. Get the length of the string using a cursor move or iterate through the string index and end the iteration. The loop displays the character of the text where the index is located (i-1).
The loop begins and iterates the length of the text until index 0 is reached.
Code Implementation
import java.lang.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class reversestring {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String stringInput = "Logicmojo";
//Get the String length
int iStrLength=stringInput.length();
//Using While loop
while(iStrLength >0)
{
System.out.print(stringInput.charAt(iStrLength -1));
iStrLength--;
}
}
}
Output
Initial string: Logicmojo Reverse String is : ojomcigoL
Code Using For Loop
Code Implementation
import java.lang.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class reversestring {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String stringInput = "Logicmojo";
//Get the String length
int iStrLength=stringInput.length();
//Using For loop
for(iStrLength=stringInput.length();iStrLength >0;-- iStrLength)
{
System.out.print(stringInput.charAt(iStrLength -1));
}
}
}
Output
Initial string: Logicmojo Reverse String is : ojomcigoL
7. By Using Stack
You can reverse a Java text using the Stack data structure by following these steps:
Make an empty collection of characters.
Use the String.toCharArray() method to convert a given string into a character array, then put each character into the stack.
Remove characters from the stack until it is clear, then return the characters to a character array. Then again, who doesn't?
Then, using String.copyValueOf(char[]), transform the character array to a string and return the formed string.
Code Implementation
import java.util.Stack;
class reversestring
{
// Method to reverse a string in Java using a stack and character array
public static String reverse(String str)
{
// base case: if the string is null or empty
if (str == null || str.equals("")) {
return str;
}
// create an empty stack of characters
Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<Character>();
// push every character of the given string into the stack
char[] ch = str.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
stack.push(ch[i]);
}
// start from index 0
int k = 0;
// pop characters from the stack until it is empty
while (!stack.isEmpty())
{
// assign each popped character back to the character array
ch[k++] = stack.pop();
}
// convert the character array into a string and return it
return String.copyValueOf(ch);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String str = "Logicmojo";
str = reverse(str);
System.out.println("Reverse String is : " + str);
}
}
Output
Initial string: Logicmojo Reverse String is : ojomcigoL
8. By Using recursion
One of the most intriguing techniques is recursively reversing a string. In this case, you must create a recursive function that accepts a single parameter, the original string. The basic condition of the function will be; if the string is null or length less than or equal to one then return the original string, else, print the last character of the string and recursively call the function. For a clearer understanding, consider the following example.
Code Implementation
import java.util.*;
public class reversestring
{
static void reverse(String stringValue)
{
if ((stringValue==null)||(stringValue.length() <= 1))
System.out.println(stringValue);
else
{
System.out.print(stringValue.charAt(stringValue.length()-1));
reverse(stringValue.substring(0,stringValue.length()-1));
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String stringValue = "Logicmojo";
System.out.println("Original string: "+stringValue);
System.out.print("Reversed string: ");
// recursive function call
reverse(stringValue);
}
}
Output
Initial string: Logicmojo Reverse String is : ojomcigoL
9. By Using Substring() Method
To recursively reverse a Java string, programmers can use the String.substring(int, int) function. Here's one method:
Code Implementation
class reversestring
{
// Method to reverse a string in Java using recursion
private static String reverse(String Str)
{
// base case: if the string is null or empty
if (Str == null || Str.equals("")) {
return Str;
}
// last character + recur for the remaining string
return Str.charAt(Str.length() - 1) +
reverse(Str.substring(0, Str.length() - 1));
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String Str = "Logicmojo";
Str = reverse(Str);
System.out.println("Reverse String is: " + Str);
}
}
Output
Initial string: Logicmojo Reverse String is : ojomcigoL
Conclusions
Strings are widely used data structures in any computer language, necessitating the use of large manipulation methods to modify them. In this article, we discussed different Java methods for reversing a string. Some are manual methods, others are built-in functions, and still others are useful classes that act on String objects. We suggest using these methods to improve the efficiency and optimization of your program.
Good luck and happy learning!






