
 Logicmojo - Updated Jan 2, 2025
Logicmojo - Updated Jan 2, 2025
What is AI?
A computer system is said to be artificially intelligent if it has been endowed with abilities that allow it to complete tasks that would generally require human intelligence. Examples of these tasks include learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception and decision-making. Much like humans, AI also gets better with time, experience, and practice.
AI makes use of a broad variety of technologies to enable a system to mimic the human process of finding a solution to a given problem; these include speech recognition, image recognition, natural language processing among many others.
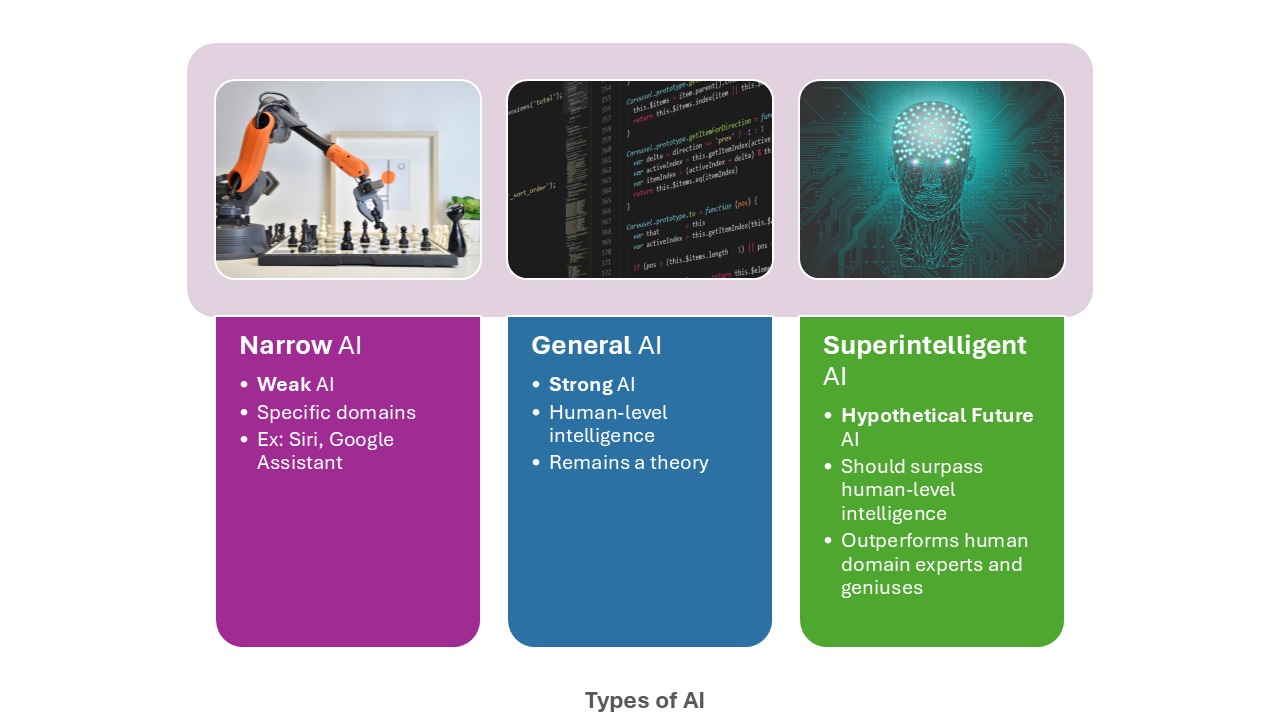
AI can be broadly classified into three types on the basis of the extent of their abilities:
Automation
AI is capable of automating repetitive operations while simultaneously reducing human error, which makes it possible for people to work on more challenging problems and innovative projects. As a result, businesses see boosts in productivity, efficiency and accuracy.Analysis
AI is especially powerful at data analysis; it can quickly recognize patterns, trends, and connections in enormous datasets that might not be immediately visible to the human eye. Businesses leverage this power of AI to gain relevant insights, make data-driven choices, and spot areas for optimization and improvement.Assistance
AI powered chatbots and virtual assistants offer immediate and individualized customer help. These sophisticated programs are able to comprehend natural language, respond to inquiries, and offer helpful advice. This enhances customer experience overall, response times, and customer service.Computation
AI systems are excellent at making decisions and solving problems since they are able to process information, evaluate many elements, and produce recommendations or solutions that are optimal. In complex fields like logistics, resource allocation, and strategy planning, this is very helpful.Personalization
AI can comprehend individual customer preferences and provide tailored experiences to each user. Recommender algorithms utilize user data to deliver personalized suggestions, recommendations, and content, which positively affects customer satisfaction, engagement, and loyalty.Critical and Strategic Thinking
Humans are capable of understanding context, anticipating consequences, and making nuanced decisions with long-term vision. They are capable of considering variables that aren’t necessarily mentioned, and of thinking outside of the box. AI can only follow patterns; humans can create them.Imagination and Creativity
While AI is capable of only regurgitating and rehashing what it's already been exposed to, humans are the ones who invent something new. Human creativity breaks boundaries that AI is unable to even see.Adaptability against Uncertainty
Humans are capable of reacting to edge cases that haven’t been defined to them. They are able to make contingent decisions on their own, without having a set of rules programmed into them to do so.Learning from Limited Data
While AI needs massive amounts of data to learn and improve its accuracy, humans are much quicker at learning from their mistakes and their experiences.Using AI
AI is only as useful as the person using it; the human sets the direction, asks the right questions, and uses the tools at their disposal alongside them with intuition and judgement.ML and DL Advancements
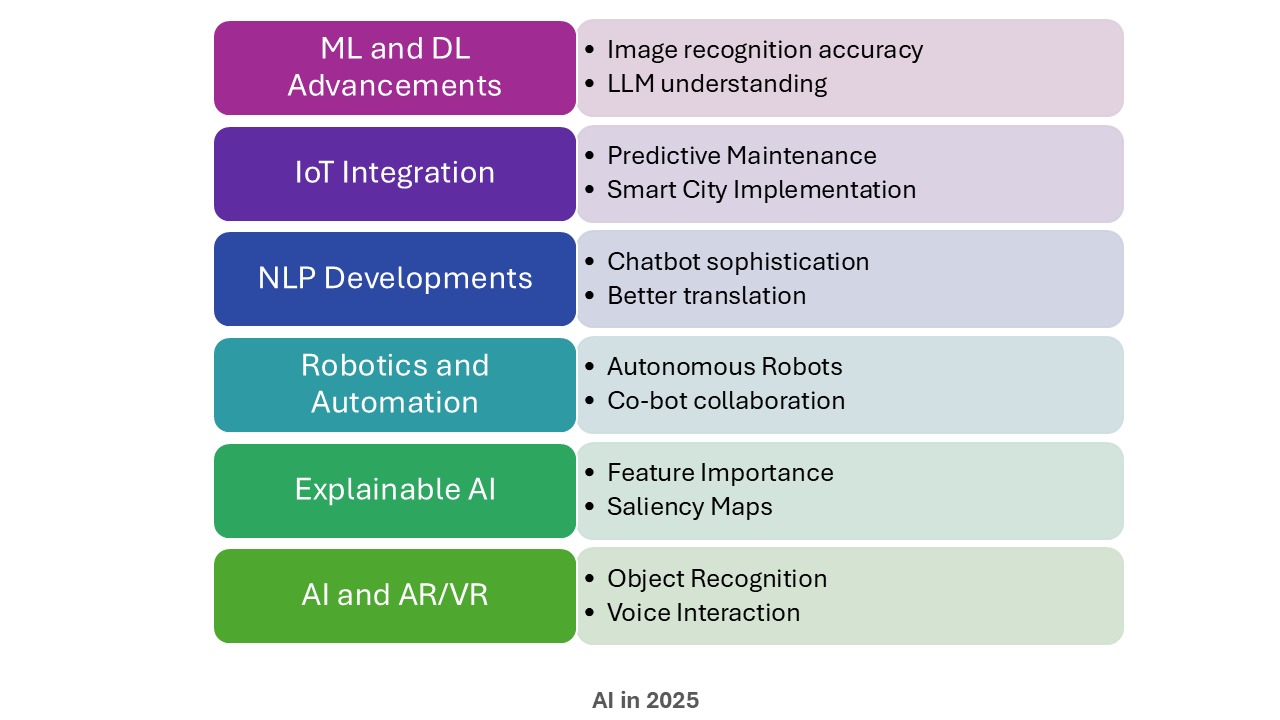
Present research and development in machine learning and deep learning algorithms will eventually lead to more sophisticated AI capabilities. AI models will become more efficient, accurate, and adaptable, allowing for more complex tasks to be automated.IoT Integration
The integration of AI with IoT devices will create a network of interconnected systems capable of collecting and analyzing vast amounts of real-time data. AI algorithms will make sense of this data, enabling smart systems to interact, communicate, and make autonomous decisions. This integration will result in more intelligent and responsive environments, with applications ranging from smart homes to smart cities and industrial automation.NLP Developments
Advancements in NLP will improve the ability of AI systems to understand and generate human-like language. This will lead to more natural and seamless interactions through voice assistants, chatbots, and language translation services. NLP advancements will also enable AI to extract valuable information from unstructured text, revolutionizing fields such as customer service, content analysis, and information retrieval.Robotics and Automation
AI-driven robotics and automation will continue to reshape industries. Collaborative robots, or 'cobots', will work alongside humans, complementing their skills and increasing productivity. These robots will perform tasks that are repetitive, dangerous, or require high precision. Industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, logistics, and agriculture will benefit from the increased efficiency, accuracy, and safety provided by AI-powered robotics.Explainable AI
Explainable AI focuses on making AI systems more transparent and understandable. It aims to provide insights and explanations on how AI systems arrive at their decisions. Explainable AI will be crucial for building trust and acceptance of AI technologies, particularly in critical decision-making processes such as healthcare and finance. It will also help organizations understand the rationale behind AI-driven recommendations, facilitating accountability and reducing the identification of biases or errors.AI and AR/VR
The integration of AI with AR/VR technologies will create immersive and interactive experiences. AI algorithms will enhance virtual environments, object recognition, and user interactions, allowing for more realistic and intelligent virtual simulations. This convergence of AI and AR/VR will have significant implications across industries, including gaming, training, education, design, and entertainment.
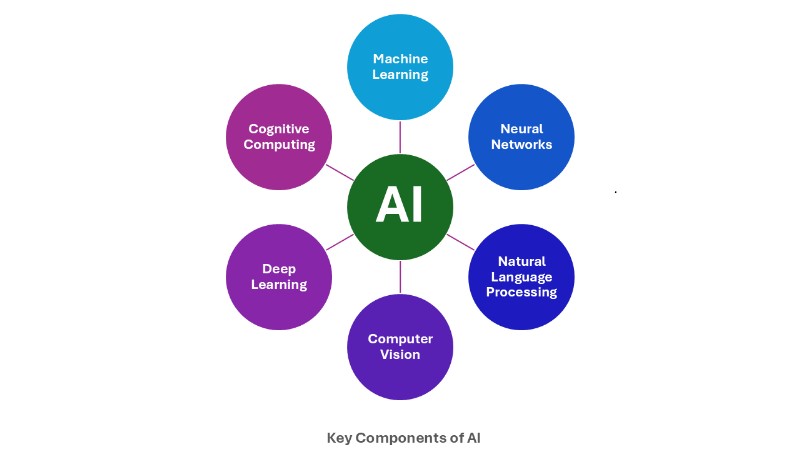
| Machine Learning | Neural Networks | Natural Language Processing | Computer Vision | Deep Learning | Cognitive Computing |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Algorithms that learn patterns from data | A type of ML inspired by the brain’s structure | Enables machines to understand and generate human language | Enables machines to interpret visual information | Subset of ML that uses deep neural networks | Simulates human thought processes to solve complex problems |
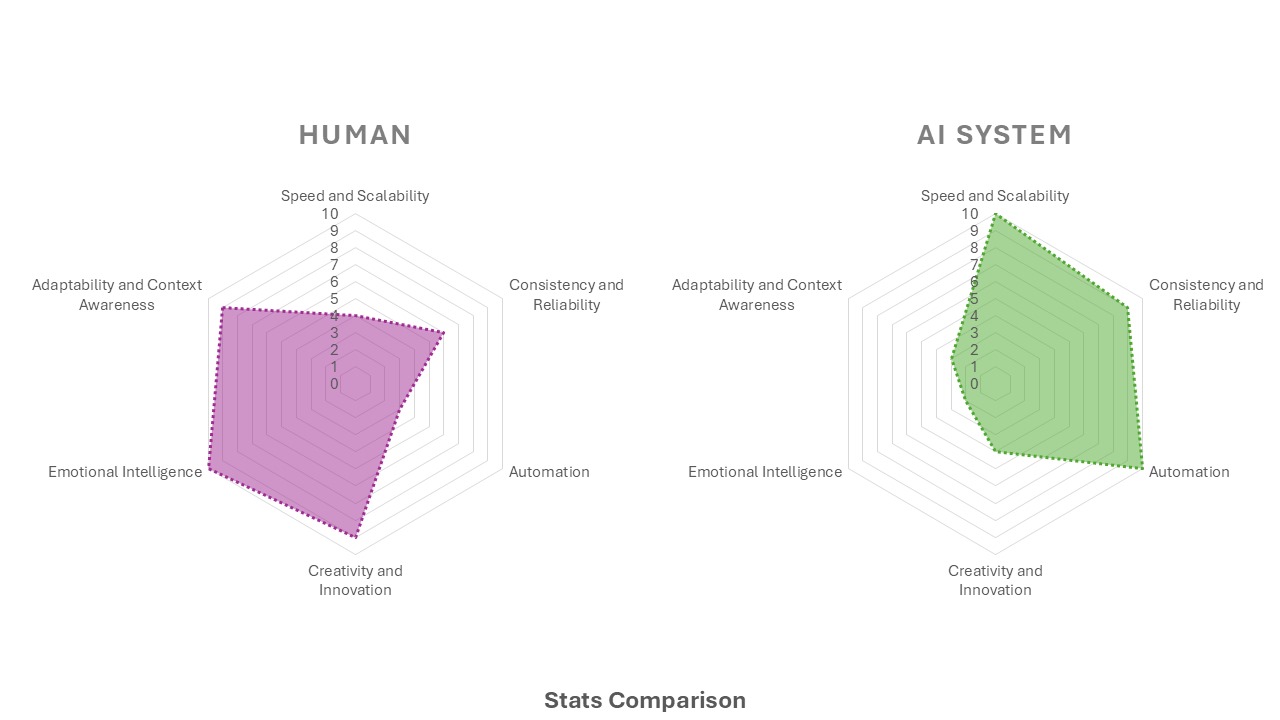
What can AI do better than you?
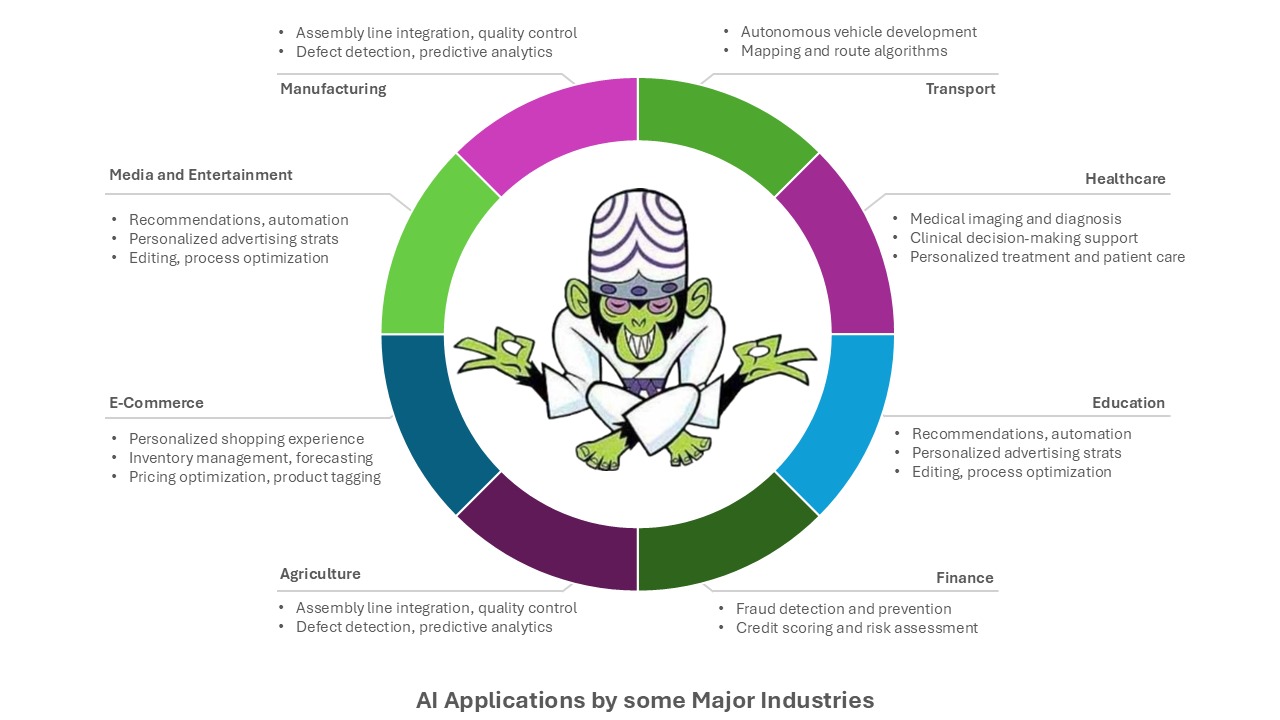
As a result of these strengths, AI, along with its more specialized subsets, have become quite indispensable in many industries today.
What can YOU do better than AI?
So, how do you learn to use AI?
Here’s a list of the top 10 AI courses in the market that we recommend to get started with AI!
| # | Course Name | Offered By | Duration | Pricing |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Artificial Intelligence Course | Logicmojo | 7 months | ₹54,000 |
| 2 | Stanford AI Professional Program | Stanford Online | 1 year | ₹1,50,000 |
| 3 | AI for Everyone | Coursera | 4 weeks | ₹3,200 |
| 4 | AI w/ Python Nanodegree | Udacity | 3 months | ₹73,000 |
| 5 | Machine Learning and AI | HarvardX | 6 weeks | Free |
| 6 | AI Engineering Certificate | IBM w/ Coursera | 6 months | ₹40,000 |
| 7 | Deep Learning Institute | NVIDIA | Flexible | ₹60,000 - ₹1,20,000 |
| 8 | Intro to Deep Learning | MIT | 4 weeks | Free |
| 9 | Deep Learning for Coders | Fast.ai | 7 weeks | Free |
| 10 | AI & ML Course | GUVI | 6 months | ₹89,999 |
What’s AI looking like in the future?
While we have made a significant amount of progress and development from the first AI that was ever built (a checkers-playing program written by Christopher Strachey and a chess-playing program written by Dietrich Prinz in 1951), there is still quite a long way to go in the future.
Conclusion
Artificial intelligence has become an integral part of various industries, transforming processes, and enhancing efficiency. Its applications span healthcare, finance, transportation, customer service, manufacturing, education, marketing, and gaming. AI offers benefits such as increased productivity, advanced data analysis, and improved decision-making. However, ethical considerations like job displacement, bias, privacy, and accountability must be addressed. The future holds promising trends, including machine learning advancements, IoT integration, NLP enhancements, robotics, explainable AI, and AI combined with AR/VR technologies. As AI continues to evolve, its impact on society and daily life will be profound.
Good luck and happy learning!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Artificial intelligence (AI) encompasses various applications that simulate human intelligence in machines, notably computer systems. Key AI applications include:
1. Expert Systems: AI systems designed to mimic the decision-making abilities of human experts in specific domains, aiding in problem-solving and decision support.
2. Natural Language Processing: AI technology that enables computers to understand, interpret, and generate human language, facilitating tasks like language translation and sentiment analysis.
3. Speech Recognition: AI systems that can transcribe spoken language into text and perform voice commands, used in virtual assistants and dictation software.
4. Machine Vision: AI-driven computer vision systems that analyze and interpret visual information from images and videos, enabling applications like facial recognition and object detection.
These applications demonstrate the diverse capabilities of AI and its potential to enhance various aspects of human-machine interaction and problem-solving.
Artificial intelligence (AI) in education brings numerous advantages for students and educators, such as:
1. Improved Accessibility: AI can adapt content and learning materials to individual students' needs, making education more inclusive and accessible to diverse learners.
2. Personalized Tutoring: AI-powered tutoring systems offer tailored lessons and feedback, helping students grasp concepts at their own pace.
3. Automated Grading and Administration: AI automates time-consuming tasks like grading assignments and managing administrative work, allowing teachers to focus more on teaching.
4. Streamlined Workflows: AI streamlines administrative processes, making it easier for schools and institutions to manage student records, schedules, and resources efficiently.
John McCarthy is widely recognized as the "father of Artificial Intelligence" due to his pivotal contributions to the field. He was an American computer scientist who not only coined the term "artificial intelligence" but also played a foundational role in its development. McCarthy, alongside other pioneers like Alan Turing, Marvin Minsky, Allen Newell, and Herbert A., laid the groundwork for the field of AI, shaping its early concepts and directions. His work continues to influence and inspire advancements in artificial intelligence today.
There are four types of AI, known as AI's four stages or categories, based on their capabilities and level of autonomy. These categories are:
1. Reactive Machines:
Reactive AI systems are the most basic type that operate purely in the present moment and have no memory or ability to learn from past experiences. They react solely based on the current input without any understanding of context or history. A famous example is IBM's Deep Blue, a chess-playing computer that defeated world chess champion Garry Kasparov in 1997. Deep Blue used brute-force computing power to evaluate potential moves but did not possess any memory or ability to learn from its past games.
2. Limited Memory:
Limited Memory AI systems have the ability to retain and recall specific past experiences or data. They can make decisions based on a combination of current and past information. A common example is self-driving cars. They use sensors and real-time data to navigate the road, but they also incorporate stored data, such as maps, traffic rules, and past experiences, to make decisions and respond to changing road conditions.
3. Theory of Mind:
Theory of Mind AI refers to systems that can understand not only their own mental state but also the mental states of others. These AI systems can interpret and predict human behavior by inferring emotions, beliefs, and intentions. While this level of AI is still largely in the research phase, it has potential applications in fields like social robotics and human-machine interactions.
4. Self-Awareness:
Self-Aware AI is the highest level of AI, where machines possess self-awareness, consciousness, and a sense of their own existence. This type of AI, often portrayed in science fiction, is still purely speculative and does not yet exist in reality.
It's important to note that the progression from one type to the next represents increasing levels of complexity and sophistication in AI systems. While Reactive Machines and Limited Memory AI are already in use today, Theory of Mind and Self-Awareness AI are still areas of ongoing research and exploration.
These four categories provide a framework to understand the capabilities and potential of AI systems, with each stage representing advancements in their ability to process information, learn, and interact with the world.
The five different types of artificial intelligence (AI) are:
1. Machine Learning: A subset of AI that focuses on training machines to learn from data and make predictions or decisions without explicit programming.
2. Deep Learning: A specialized form of machine learning that uses neural networks with multiple layers to process and analyze complex data, often used in tasks like image and speech recognition.
3. Natural Language Processing (NLP): AI technology that enables machines to understand, interpret, and generate human language, crucial for tasks like chatbots and language translation.
4. Computer Vision: AI that allows machines to interpret and understand visual information from images and videos, used in applications like facial recognition and object detection.
5. XAI (Explainable AI): An emerging field focused on making AI systems more transparent and understandable, ensuring that AI decisions can be explained and trusted.
Artificial intelligence (AI) has numerous applications in business, particularly in finance and accounting, including:
1. Automation of Financial Processes: AI can automate various financial tasks such as data entry, invoice processing, and expense management, improving accuracy and efficiency.
2. Fraud Detection: AI-powered algorithms can analyze transactions in real-time to detect and prevent fraudulent activities, enhancing security in areas like e-commerce.
3. Financial Forecasting: AI can analyze historical data and market trends to generate more accurate financial forecasts, aiding in better decision-making and risk assessment.
4. Customer Service: AI-driven chatbots and virtual assistants can provide 24/7 support, address customer inquiries, and streamline customer interactions, enhancing overall customer experience.
5. Personalized Marketing: AI can analyze customer data to create personalized marketing campaigns, improving customer engagement and conversion rates.
6. Supply Chain Optimization: AI helps optimize inventory management, demand forecasting, and logistics, reducing costs and improving supply chain efficiency.
7. HR and Talent Management: AI can assist in recruitment, employee onboarding, and performance analysis, helping organizations manage their workforce more effectively.
8. Data Analytics: AI-driven analytics tools can sift through vast datasets to uncover insights and patterns, facilitating data-driven decision-making in various business functions.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has found several applications in agriculture, enhancing various aspects of the industry:
1. Crop Production: AI-driven systems can optimize planting techniques, irrigation, and fertilization by analyzing data to maximize crop yield and quality.
2. Real-Time Monitoring: Sensors and AI enable real-time monitoring of environmental conditions, helping farmers make timely decisions regarding factors like weather, soil moisture, and pest infestations.
3. Harvesting and Processing: AI-powered machinery and robots can autonomously harvest crops and sort them based on quality, increasing efficiency and reducing labor costs.
4. Weed Detection: AI algorithms can identify and target weeds, allowing for precise and efficient weed control, reducing the need for herbicides.
5. Yield Detection: AI can predict crop yields accurately, aiding in better resource allocation and market planning.
6. Crop Quality: AI systems assess crop quality by analyzing factors such as size, color, and disease presence, ensuring that only the highest-quality products reach the market.
7. Market Planning: AI can analyze market trends and demand, helping farmers and producers make informed decisions about when and where to sell their products.
AI in India has its roots dating back to the 1960s:
1. Professor H.N. Mahabala: Professor H.N. Mahabala played a pioneering role in introducing AI to India during the 1960s. His work and contributions laid the foundation for AI research and development in the country.
2. Knowledge-Based Computing Systems (KBCS): In 1986, the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) initiated the creation of Knowledge-Based Computing Systems (KBCS) in India. This development marked a significant step in promoting AI research and education in the country.
These early initiatives, led by individuals like Professor H.N. Mahabala and supported by organizations such as UNDP, paved the way for the growth of AI in India, fostering research, education, and innovation in the field.
Google Assistant is indeed one of the most popular and advanced virtual assistants globally, and several factors contribute to its popularity:
1. Advanced Natural Language Processing: Google Assistant boasts sophisticated natural language processing capabilities, enabling more natural and conversational interactions with users.
2. Integration Across Devices: It seamlessly integrates with a wide range of devices, including smartphones, smart speakers, and smart home appliances, making it accessible to a broad user base.
3. Extensive Knowledge Base: Google's vast database and search capabilities empower Google Assistant to provide accurate and up-to-date information on a wide array of topics.
4. Multilingual Support: It supports multiple languages and is available in various regions, increasing its accessibility to a global audience.
5. Third-Party App Integration: Google Assistant supports a multitude of third-party apps and services, enhancing its versatility and utility for users.
6. Continuous Development: Google continually invests in the development and improvement of Google Assistant, introducing new features and capabilities regularly.
7. Voice Recognition: Its accurate voice recognition technology allows for convenient hands-free operation and voice commands.
8. AI Ecosystem: Google Assistant is part of Google's larger AI ecosystem, benefiting from the company's extensive research and resources in artificial intelligence.
